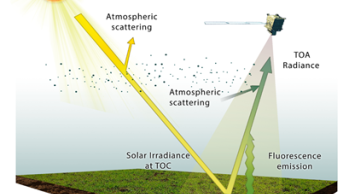
Plants emit a faint, infrared glow as a by-product of photosynthesis, known as solar induced fluorescence (SIF). This signal can be detected from space using spectrometers onboard Earth-orbiting satellites. SIF serves as a valuable proxy for photosynthetic activity, offering crucial insights into the global carbon cycle. It is also an important indicator of plant health and can support crop monitoring and drought risk assessment.
Category: Research Insights
Grassland community types in sustainable land management and the maintenance of pastoralist livelihoods
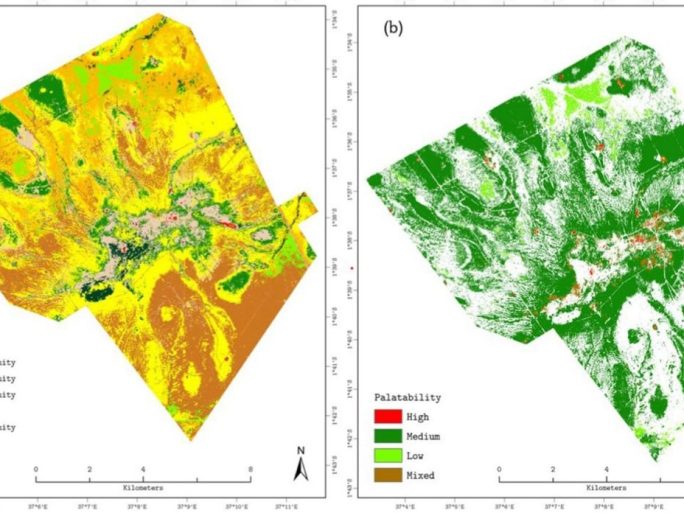
Today is World Environment Day and we are celebrating by research summary of a recent paper co-authored by our own Professor Heiko Baltzar. The study, published in Frontiers (Front. Sustain. Food Syst., 27 May 2025. Sec. Land, Livelihoods and Food Security) last month, explored the role of grassland community types in sustainable land management and the maintenance of pastoralist livelihoods in Kenya. Semi-arid grassland ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and animal fodder; but are increasingly placed under pressure by overgrazing and climate variability. The aim of the study was to map grassland communities and assess their palatability in semi-arid Kenya using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA) and sentinel-2 satellite imagery. They also imbedded species abundance with forage quality metrics. Their findings provide actionable insights for sustainable grazing management and land protection.
Hazardous Weather
In our changing climate, hazardous weather events such as storms, floods, wind, snow and ice, and fog events are expected to become more extreme. Our ability to manage these hazards is dependent on timely and accurate weather forecasts.
Ocean biogeochemistry
Ocean biogeochemistry and ecosystems are an essential Earth system component, both because of their uptake of antrophogenic carbon emissions (through biological carbon pump, i.e. air-sea fluxes, photosynthesis in the ocean and transport of carbon to the ocean bottom) and for providing living resources for billions of people around the world.
Sea Ice Data Assimilation
Arctic sea ice is a crucial component of the climate system. The radiation balance and the dynamics of the atmosphere and ocean have strong interactions with sea ice. Observations show that the extent of Arctic Sea ice has been declining over the last few decades. This could have a significant impact on the climate, ecosystems and human activities and highlights the need for improved sea ice prediction.
4DEnVar Data Assimilation Technique
Land surface models are paramount to the climate modelling community in that they provide ‘boundary conditions’ — a quantification of the water, carbon and energy fluxes between the land and atmosphere at the Earth’s surface. Arguably the biggest problem for land surface modellers is the selection of parameter values for use in their land surface model.
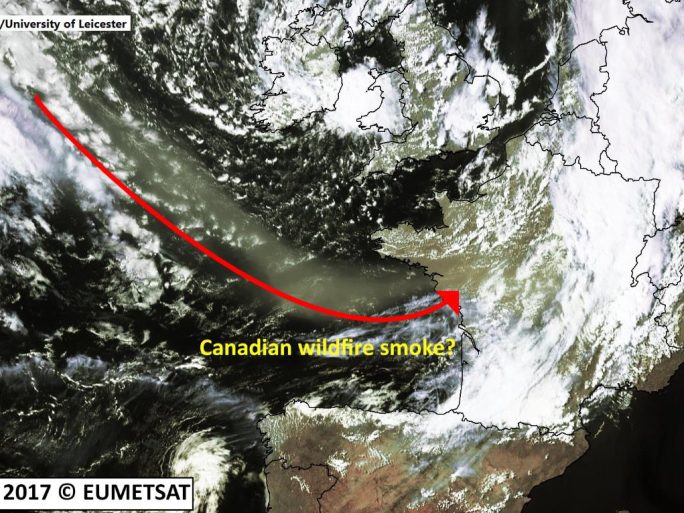
Canadian Wildfires Campaign
Earth observation is vital in air quality modelling and assessments, particularly in regions where substantial and reliable ground networks are unavailable. The King’s NCEO team have produced algorithms that utilise satellite observations of active fires to estimate emissions of fire-sourced particulate matter.
Carbon Monoxide/Reactive trace gases
Long-term satellite observations of carbon monoxide and other reactive trace gases in the atmosphere help us to understand the role of these gases in a changing climate and the change in these gases over time.
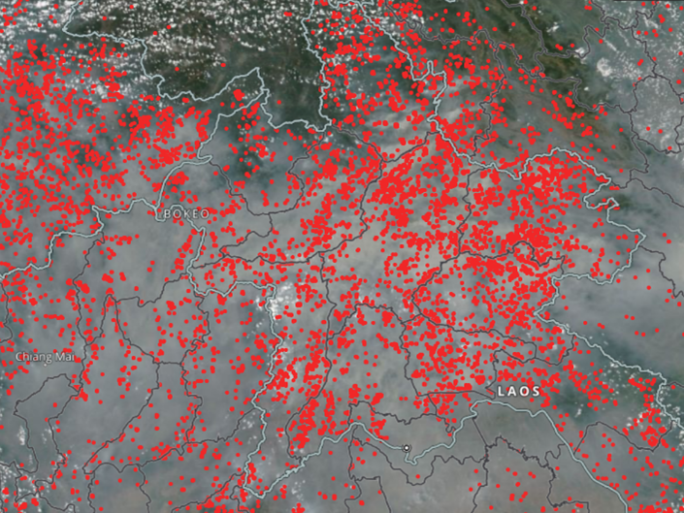
Air Quality Research in Southeast Asia
Global and regional atmospheric models suggest that every spring, air quality in parts of Northern Southeast Asia is amongst the worst in the world, apparently due to smoke from biomass burning.
Air quality impacts from fires
Earth observation is vital in air quality modelling and assessments, particularly in regions where substantial and reliable ground networks are unavailable.
Aerosol-cloud-precipitation interactions
The National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) has secured five years of investment in its environmental science research capabilities through the NERC’s National Capability Single Centre Science and National Public Good initiatives.
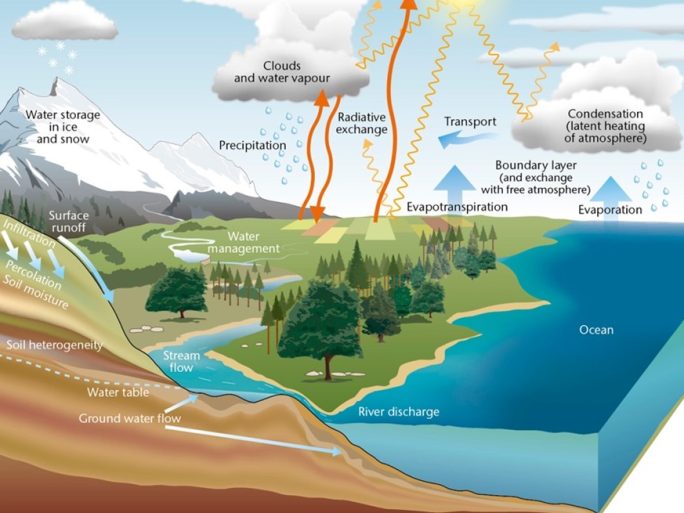
Water Cycle
The National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) has secured five years of investment in its environmental science research capabilities through the NERC’s National Capability Single Centre Science and National Public Good initiatives.
Landscape Carbon Dynamics and Modelling
The National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) has secured five years of investment in its environmental science research capabilities through the NERC’s National Capability Single Centre Science and National Public Good initiatives.
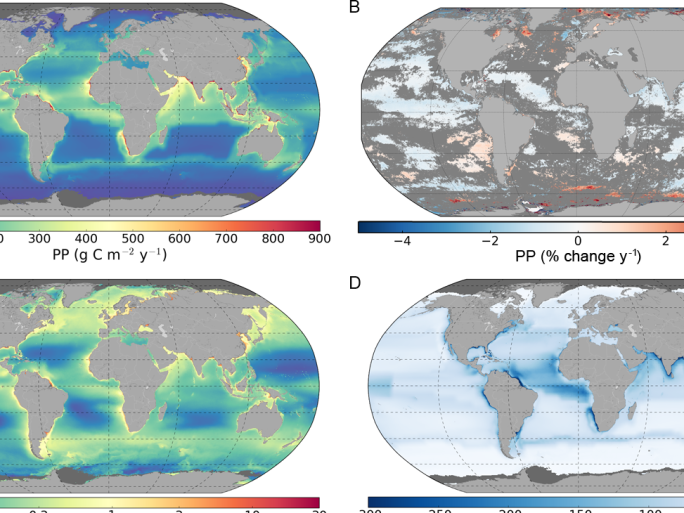
Carbon Cycle Monitoring Ocean Carbon Pools and Fluxes
The National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) has secured five years of investment in its environmental science research capabilities through the NERC’s National Capability Single Centre Science and National Public Good initiatives.
Terrestrial Laser Scanning
The National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) has secured five years of investment in its environmental science research capabilities through the NERC’s National Capability Single Centre Science and National Public Good initiatives.
Climate changes at 2°C warming as seen in the UK Earth System Model
This NCEO-led joint study with UK Earth System Model (UKESM) developers showcases the changes in future climate at different Global Warming Thresholds (GWTs) as seen in projections made with the UKESM1 model